Common Equine Health Issues And How To Prevent Them?
Common Equine Health Issues And How To Prevent Them?
Common Equine Health Issues And How To Prevent Them? Horses are giant Animals that need attentive care to maintain their health and well-being. Like all living beings, they are prone to different health issues that can affect their quality of life if not treated properly. Understanding these common health concerns and taking preventative measures can help ensure your horse leads a healthy and happy life.
Colic:

One of the horses' most common health problems is colic, which is abdominal pain. Colitis can range from mild discomfort to a life-threatening condition. Different factors, including changes in diet, dehydration, ingestion of sand or foreign objects and intestinal blockages can cause it. To prevent colic, providing your horse with a consistent feeding schedule and ensuring they have access to clean water at all times is essential. Regular exercise also helps maintain a healthy digestive system. Additionally, avoid sudden changes in diet and ensure the horse’s feed is free from mold or contaminants. Regular dental check-ups are important as poor dental health can contribute to colic.
Lameness:
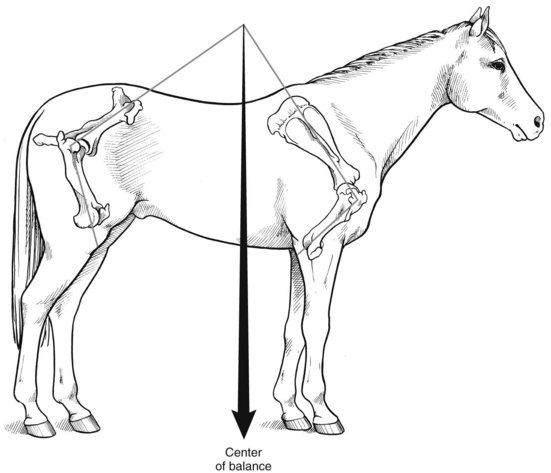
Another common problem in horses is lameness, which can result from injuries, infections or chronic conditions such as arthritis. Other contributing factors include fractures, muscle damage, neurological disorders and poor limb conformation. Lameness can severely impact a horse’s flexibility and performance. To reduce the risk of lameness, it is essential to maintain a regular hoof care routine, including trimming and shoeing as needed. Providing your horse with appropriate footing and avoiding overexertion are key preventative actions. If you notice any signs of discomfort or abnormal gait, consult a veterinarian on time to address the issue before it worsens.
Respiratory Issues:
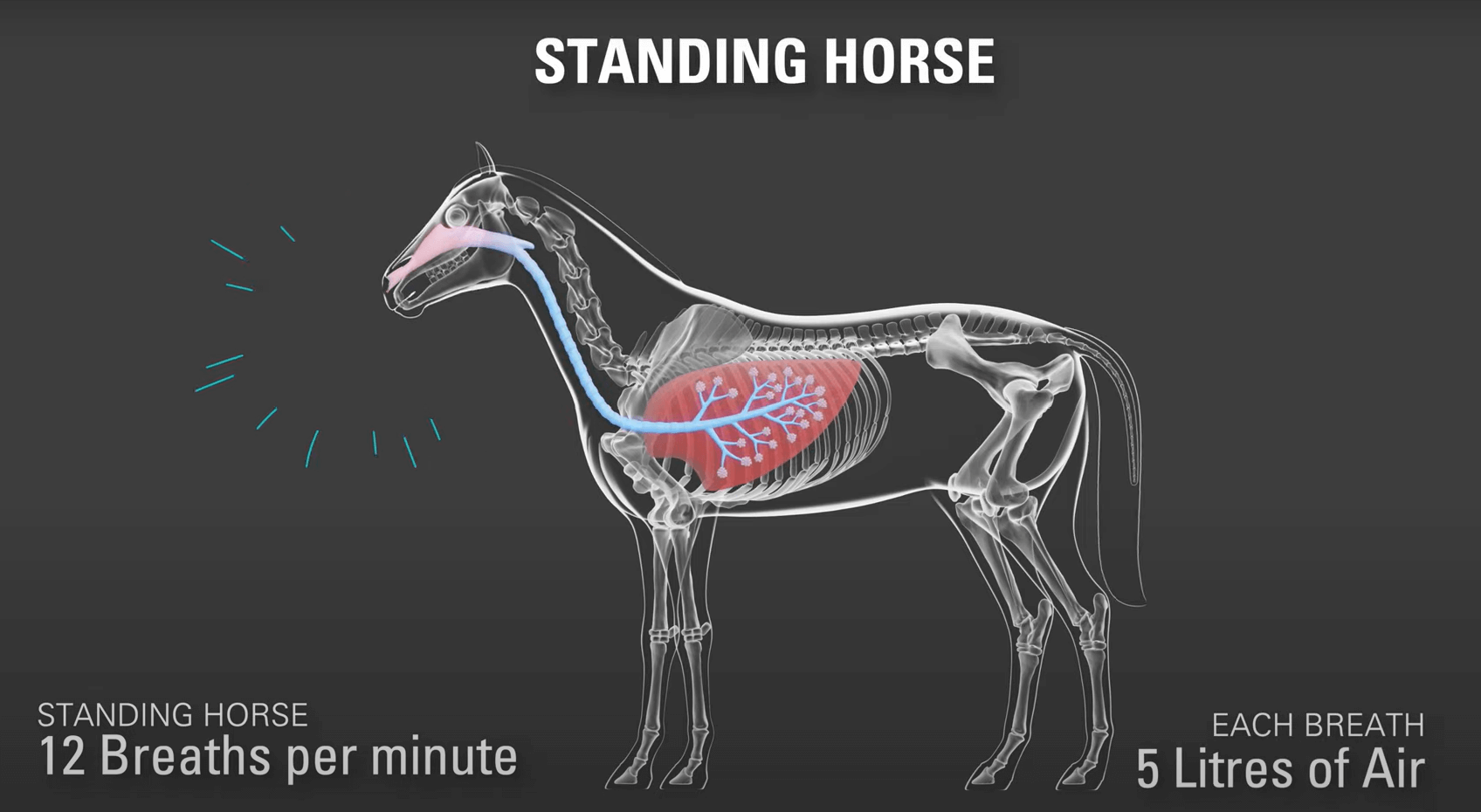
Respiratory issues are another major problem for horses. Horses can develop respiratory problems due to poor air quality, dust, mold or infectious diseases. Common respiratory problems include infections like equine influenzas and strangles and chronic conditions. Conditions like heaves, similar to asthma in humans, can significantly impact a horse’s breathing. To minimize the risk of respiratory issues, ensure your horse’s living environment is well-ventilated and free from excessive dust and mold. Feeding hay that is clean and not overly dusty can also help. Vaccinations protect your horse from infectious respiratory diseases, so an up-to-date vaccination schedule is essential.
Parasite Infestations:
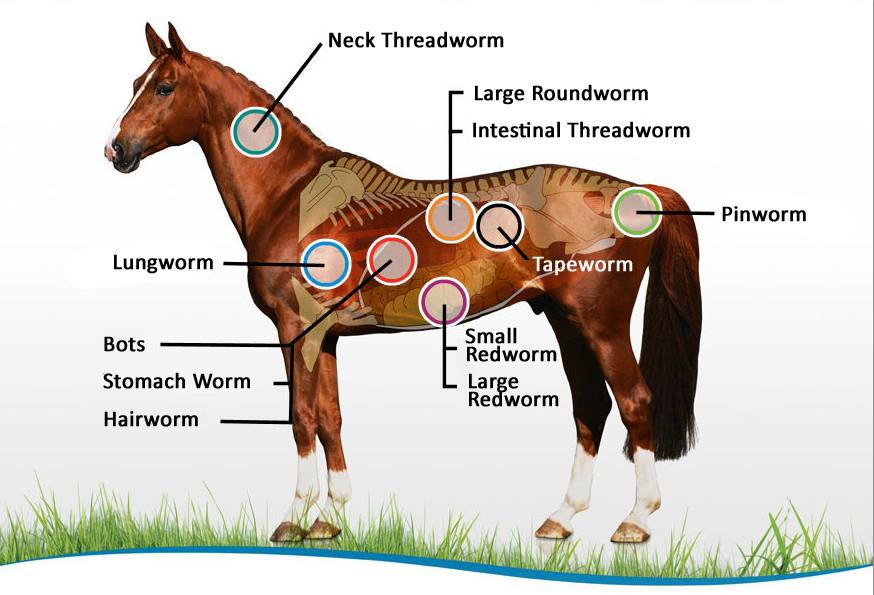
Parasite infestation in horses is a common health concern affecting their overall well-being, growth and performance. Internal parasites such as large and small enormously, roundworms, tapeworms and bots. Parasite infestations, such as those caused by worms, can lead to heavy weight loss, colic and a dull coat. External parasites such as flies, mites and ticks cause skin irritation, hair loss and sometimes allergic reactions. Regular deworming and faecalis tests can help manage and prevent parasite issues. It is also essential to maintain clean living conditions, as unsanitary environments can increase the risk of parasite exposure. Rotating pastures and avoiding overcrowding are additional strategies that can help reduce the chances of an infestation.
Skin Conditions:
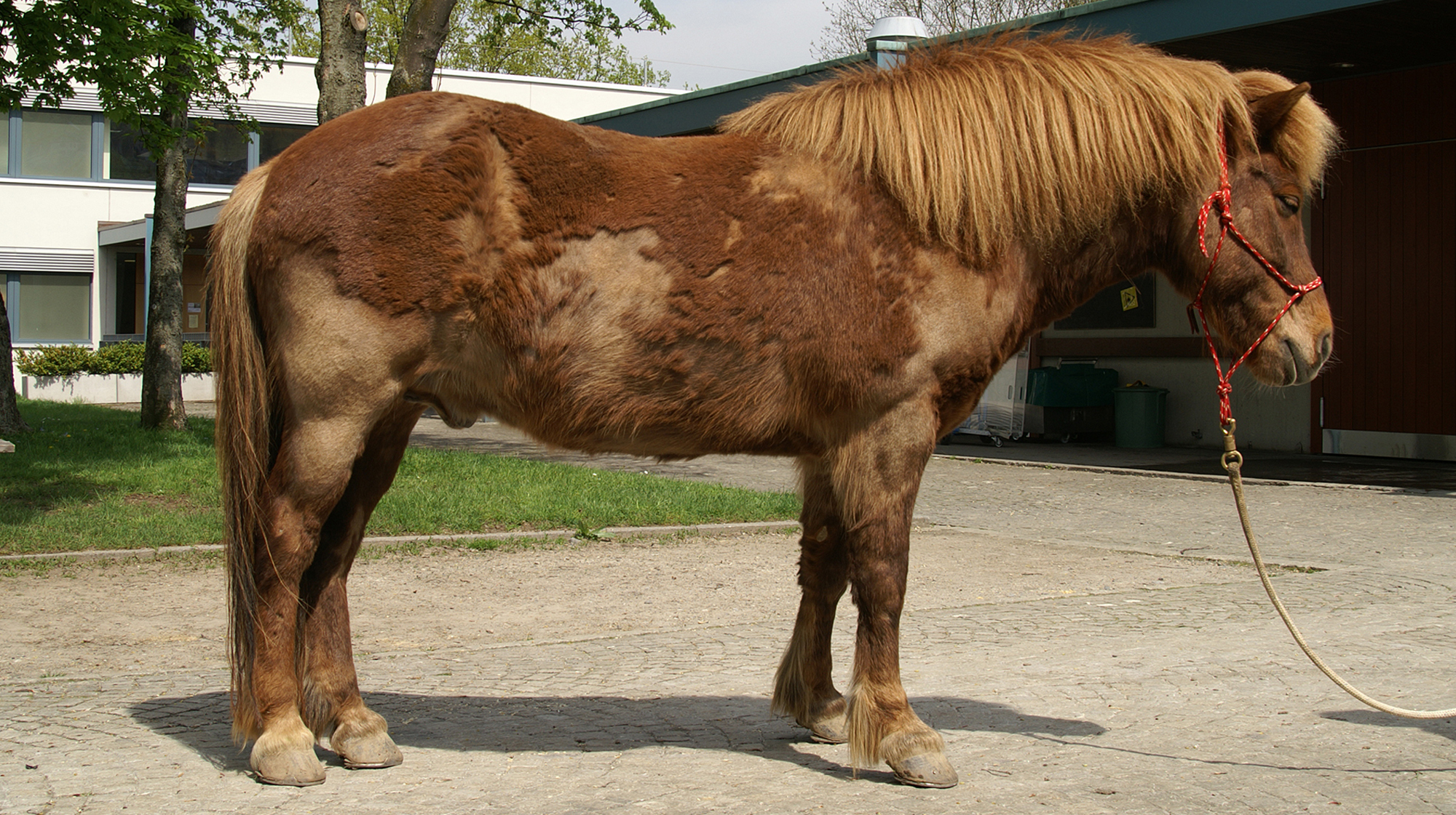

Skin conditions are another common problem in horses. Problems like rain rot, mud fever, and sweet itch can cause discomfort and irritation. Fungal infections like ringworm lead to circular patches of hair loss and scaly skin. These conditions are often caused by environmental factors such as excessive moisture, insect bites and poor hygiene. To prevent skin problems, ensure your horse is groomed regularly and kept dry during rainy or wet weather. Using fly repellents and providing adequate shelter can also reduce the risk of insect-related conditions. If a skin issue does occur, early treatment is essential to prevent it from worsening. Treatment depends on the cause and may include medicated shampoos, topical ointments, antifungal or antibacterial treatments and veterinary-prescribed medications for severe cases. Horse owners can promote healthy skin and prevent complications by addressing skin conditions early and maintaining good hygiene.
Dental Health:
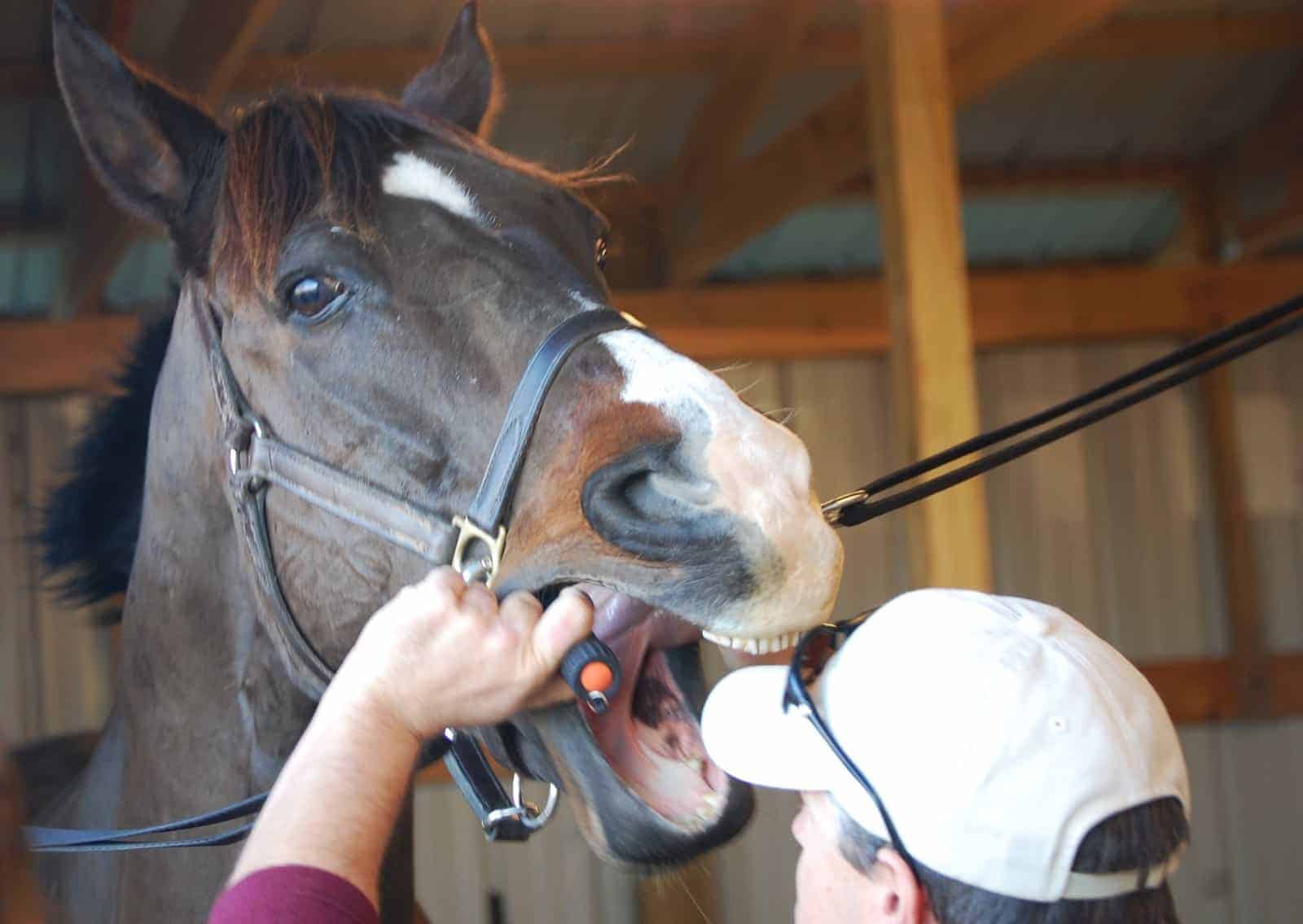
Dental health is an often overlooked aspect of horse care. Problems such as sharp edges on teeth, swellings, or loose teeth can make it difficult for a horse to eat, leading to weight loss or colic. Common dental issues include retained caps in young horses, abscessed teeth and periodontal disease in horses. Regular dental check-ups by an equine dentist or veterinarian are essential for maintaining healthy teeth and preventing oral issues. Observing your horse for signs of difficulty chewing or dropping food can also help catch dental problems early. Good dental care ensures that horses can chew their food efficiently, aiding digestion and nutrient absorption. Horse owners can enhance their horses' comfort, performance, and longevity by staying proactive with routine dental check-ups and promptly addressing problems.
Laminitis:

Another significant concern is laminitis, a painful and potentially debilitating condition affecting the hooves. It involves inflammation of the laminae, the tissue connecting the coffin bone to the hoof wall. This inflammation weakens the bond, potentially leading to the rotation or sinking of the coffin bone, a condition known as founder. Laminitis can be caused by overeating grain or lush posture, overweightness or underlying metabolic conditions. To prevent laminitis, carefully managing your horse’s diet and avoiding excessive sugary or starchy feed intake is essential. Maintaining an appropriate body weight and providing regular exercise are also vital. If your horse shows signs of laminitis, such as unwillingness to move or a noticeable change in hoof structure, seek veterinary care instantly.
Eye issues:

Horses are also prone to eye infections, injuries and conditions like conjunctivitis. It is common and can range from minor irritations to severe conditions that may threaten vision. Eye problems can quickly intensify if not treated on time. To protect your horse’s eyes inspect them regularly for signs of redness, swelling or discharge. Keeping their living area clean and free from sharp objects can reduce the risk of injuries. Fly masks can also provide protection from insects and debris that could irritate the eyes. Symptoms of eye problems include squinting, excessive tearing, eye discharge, cloudiness or swelling around the eye. Horses may also show discomfort by rubbing their eyes or acting sensitive to light.
Nutritional Deficiencies:

Nutritional deficiencies are another concern, as they can lead to various health problems, including poor coat condition, weak hooves and a compromised immune system. Providing a balanced diet tailored to your horse’s age, activity level, and health needs is essential. Consulting with an equine nutritionist or veterinarian can help ensure your horse receives the necessary nutrients.
Conclusion:
Preventing common equine health issues requires a proactive approach and a deep eye for any signs of discomfort or illness. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of possible problems. Caring for a horse requires dedication and attention to detail. While health challenges are expected, being prepared and knowledgeable about preventative measures can help your horse flourish and build a rewarding partnership with this remarkable animal.


















